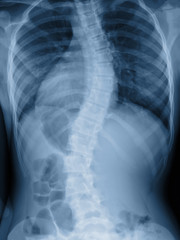
Have you been diagnosed with congenital scoliosis, or do you know someone who has? People are affected by this very uncommon ailment from the moment they are born, and it may continue to provide unusual difficulties for the rest of their lives. In this article, we will explore the complexities of congenital scoliosis, including its origin and cause, symptoms, and the many treatment options that are now available.
What are the Variations of Scoliosis that are Present at Birth?
Congenital Scoliosis is made up of several variations of scoliosis that are present at birth and may take many different forms, depending on which areas of the spine are afflicted and in what manner. The following are some examples of congenital forms of scoliosis:
- Congenital scoliosis of the hemivertebrae type develops when a vertebra in the spine fails to grow on one side, resulting in a vertebra that is wedge-shaped. This condition is often present at birth. A curved spine may be the result of the presence of hemivertebrae, which may develop in any section of the spine.
- Butterfly vertebrae is a kind of congenital scoliosis that is caused by the failure of two parts of a vertebra to fuse together during the process of fetal development. This results in the vertebrae taking on the appearance of a butterfly. Butterfly vertebrae are another possible contributor to a curved spine.
- Congenital scoliosis with wedge vertebrae is characterized by the development of a vertebra with a triangular form during fetal development. A curvature of the spine may result from the wedge form.
- Another type of congenital scoliosis is known as a congenital bar, and it develops when a bone bar links two or more vertebrae, preventing the vertebrae from moving correctly. The curvature in the spine is often caused by the vertebrae that are fixed in place.
What are the Symptoms of Congenital Scoliosis?
The degree and location of the spinal deformity may have a significant impact on how the individual experiences the symptoms of congenital scoliosis. The following are examples of some frequent symptoms:
- Disparity in the shoulders or the waistline,
- A difference in height between the two hips,
- A rib cage that is not symmetrical,
- Difficulty breathing due to pressure on the lungs,
- Discomfort in the back or the legs,
- Symptoms of tingling or weakness in the legs
How is Congenital Scoliosis Diagnosed?
There are a few ways that experts will diagnose this condition. A physical examination and other imaging studies are often required to arrive at a diagnosis of congenital scoliosis. Throughout the course of the physical exam, your physician will evaluate the curvature of your spine, as well as its range of motion and any physical abnormalities that may be present. Imaging procedures, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, are used to view the structure of the spine and detect any abnormalities that may be present.
What are the Treatments Available for Children Born with Scoliosis?
The degree of the curvature and the patient’s age are both factors that are considered while developing a treatment plan for congenital scoliosis. Keeping an eye on adolescents who have mild cases of scoliosis is probably the best course of action since the disease may not become worse. Treatment options for situations that are more severe include the following:
The Usage of Braces: Braces are able to be used to prevent additional curvature of the spine and may be worn until the spine has finished developing.
Surgery: Scoliosis surgery may be required in situations where the condition is severe or when it continues to worsen despite the use of bracing. Spinal fusion or the insertion of growth rods are two surgical treatments that may be considered.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may assist in improving a person’s posture, as well as their strength and flexibility.
Summary: What is Congenital Scoliosis?
A rare spinal malformation known as congenital scoliosis is present from birth. It happens as a result of aberrant spine growth during fetal development. Congenital scoliosis, in contrast to other types of the condition, is brought on by spinal abnormalities that happen in the first six weeks of pregnancy.
Congenital scoliosis is caused by spinal abnormalities, such as missing or fused vertebrae, hemivertebrae, or butterfly vertebrae. These anomalies may cause the spine to twist and bend unusually, causing a variety of symptoms, such as unequal shoulders or hips, a noticeable spine curvature, and in more severe instances, perhaps breathing problems.
Depending on the degree of spinal deformity and the location of the curvature, congenital scoliosis severity might change. That said, observation, bracing, and surgery are all possible treatments for congenital scoliosis, depending on the person’s symptoms and general health. Many people with congenital scoliosis are able to live healthy, active lives with early diagnosis and the right treatment.
Speak to one of our Pediatric Scoliosis Medical Experts
Talk to one of our medical experts if you or a loved one has any reason to think that they may have congenital scoliosis. We would be happy to meet with you personally and talk about your concerns. Give us a call to get started.